We are providing you with the Updated and Latest Interview Questions and Answers for Civil Engineering Competitive Examinations.
Please take time to review this Civil Engineering interview Examinations questions with the answers.
Interview Questions and Answers for Civil Engineering Competitive Examinations
1. What are the causes of building collapse?
The Passage of time is one reason. Buildings also collapse due to weak foundations. Earthquakes, hurricanes and other natural disasters can also damage the structure of the buildings and cause it to collapse. Bombings or demolition of buildings is also other reasons.
2. What are the applications of modulus of elasticity?
As the term implies, "Modulus of Elasticity relates to the elasticity or "flexibility" of a material. The value of modulus of elasticity is very much significant relating to deflection of certain materials used in the construction industry. Take for example the general E value of mild carbon steel is about 200 GPA compared to
about 70 GPA for aluminum. This simply translate that aluminum is 3 times flexible than steel.
3. What is the difference between routing maintenance and major maintenance in school facilities?
The routine maintenance is the minor and consistent repairs that are engaged in the school premises. Examples could include Painting, replacement of fixtures, louver blades, furniture repairs, and Patching cracks in the school buildings.
The major maintenance could also be a total rehabilitation of the school, either school buildings or any other project within the school community. It could be total restructuring of the lighting system in the school or sanitary system.
4. How are freeway bridges built?
After calculating the anticipated traffic for the bridge, cement/reinforced- with- rebar stanchions are spaced over the freeway to accommodate the bridge. An 'off-ramp' from the freeway to the bridge is constructed, as is an 'on-ramp' to the subsequent road. Cement/rebar slabs are built and lifted with cranes to form the
platform, and voila! Drive carefully.
Although the bridge deck/roadway is almost always a concrete slab, the structure that holds up the bridge deck can be reinforced concrete, structural steel, or a combination of steel and concrete.
5. What is the difference between absorption & adsorption and sorption?
Absorption generally refers to two phenomena, which are largely unrelated. In one case, it refers to when atoms, molecules, or ions enter some bulk phase - gas, liquid or solid material. For instance, a sponge absorbs water when it is dry.
Absorption also refers to the process by which the energy of a photon is taken up by another entity, for example, by an atom whose valence electrons make transition between two electronic energy levels. The photon is destroyed in the process. The absorbed energy may be re-emitted as radiant energy or transformed into heat energy.
The absorption of light during wave proPAgation is often called attenuation. The tools of spectroscopy in chemistry are based on the absorption of photons by atoms and molecules.
Adsorption is similar, but refers to a surface rather than a volume: adsorption is a process that occurs when a gas or liquid solute accumulates on the surface of a solid or, more rarely, a liquid (adsorbent), forming a molecular or atomic film (the adsorb-ate). It is different from absorption, in which a substance diffuses into a
liquid or solid to form a solution.
6. How do you measure concrete?
Cubic feet, Cubic yards, Cubic Meter
7. Which is stronger solid steel rod or hollow steel pipe?
On a per pound basis, steel pipe is stronger in bending and is less likely to buckle in axial compression.
8. What is the tallest man made structure in the world?
The tallest man made structure is the KVLY-TV mast which is 2063 feet tall. The worlds tallest man made structure is Burj Dubai which is 800 meter tall.
9. What are the uses of alloys in daily life and how are alloys made?
Alloying is not always done to produce a 'superior' material, but to produce materials having a desired requirement in the industry or elsewhere. A classic case is of lead solder (containing lead & tin), in which the melting point of the constituent elements are lowered, not necessarily a desirable property.
Alloying can be carried out using hot press method (a sheet of material is sandwiched with alloying material), rolling the heated base metal in a drum full of alloying metal powder, using hot spraying, galvanizing (dipping the base in a molten solution of alloying material) etc. Sometimes the alloying material is added in small
proportions to the molten base metal (e.g., in production of different types of steel).
10. What is the worlds largest concrete dam?
The Grand Coulee Dam is said to be the largest concrete dam. Currently the world's largest concrete dam is the Itaipu Dam, an accomplishment of two neighboring countries, Brazil and PAraguay in South America.
Though it is not finished yet, the Three Gorges (or Sandapong) Dam on the Yangtze River in China will take over as the largest upon its completion, which is slated for 2009.
11. What is braced excavation all about?
Excavations are braced to prevent the cave-in of surrounding unstable soil.
12. What is the meaning of soil reinforcement?
Soil reinforcement is the act of improving soil strength to enable it support or carry more load.
Two common examples are:
a) Mixing a soil amendment such as lime into weak clayey soil and re-compacting to improve soil-bearing capacity (often done under the road base in highway construction)
b) Installing plastic or composite webbing layers (called geogrid material) alternating with compacted soil to produce a stronger sloped soil structure (often done on steep roadway embankments to improve strength and stability)
13. What is aggregate?
Aggregate is the component of a composite material used to resist compressive stress.
14. What year was the keystone power plant in Indiana County constructed?
1967 began commercial operation on unit 1.
15. What is the force exerted by the Tacoma narrows bridge?
The force exerted to the Tacoma narrows bridge was initially the wind resistance. The wind resistance caused the whole bridge to act as a system with forced vibration with damping.
16. How do you calculate the power of a centrifugal pump?
The input power, that is, the power required to operate the pump should be stated in Hp (horsepower) on the pump's nameplate. It can also be calculated by the 3-phase power equation:
P(in Hp) = VI(1.7c) = Rated Voltage x Rated Current x 1.73/ %Efficiency
If this is a consumer grade pump that operates on 120Vac, then the equation becomes P = VI, simply multiply the operating voltage, 120 x current (which is the number followed by the letter "A".
The output power, which really is not technically power, but rated in Gpm (gallons per minute), or capacity should also be on the nameplate. If you have the make, model, and (not necessarily needed) the serial number (also on the nameplate) you could call the manufacturer's customer service dept. As an application engineer, I have contacted countless manufacturers, and service dept's for assistance. It is now big deal to them, they will be happy to answer your questions.
17. Why nautical mile is different from statute mile?
One nautical mile is defined by one latitude minute of arc (there are 60 such minutes to a degree). This equals 1852 meters, and roughly (but coincidentally) 2000 yards or 6000 feet. (Edit: actually, a standard nautical mile is 6076 feet, 6000 feet and 2000 yards are commonly used approximations, but produce an error of about 1%).
The statute mile had a little fuzzier definition to start with, as one mile was the same as 1000 roman PAces/steps. The definition has since changed, but one statute mile equals about 1609 meters.
18. What is rigging?
In sailing, the ropes used to move the sails around so the boat will move in the right direction when the wind blows.
19. What is absolute pressure?
Absolute pressure is simply the addition of the observed gage pressure plus the value of the local atmospheric pressure.
20. How do we calculate absolute pressure?
Absolute is equal to gauge pressure plus atmospheric.
21. What is Gravity flow?
Gravity flow is fluid flowing due to the forces of gravity alone and not to an applied pressure head. In the Bernoulli equation, the pressure term is omitted, and the height and velocity terms are the only ones included.
22. What is horizon or horizontal mining?
Horizon or horizontal mining can be applied to extraction of material from seams of any stratified mineral such as limestone or ironstone, but it is more usually
associated with coal - PArticularly where there are several seams that are inclined or folded and/or faulted.
Horizon mining involves long level roadways (horizons) being driven from the shafts to the extremity of the area to be mined.
The levels of the horizons are chosen to intersect the maximum number of seams the maximum number of times. As the seams are intersected, headings will be driven into the seam so that the desired material may be extracted. This method of mining requires a thorough understanding of the geological structure of the area to be mined so that the level of the horizons can be chosen for optimum results.
This method of mining is popular in modern coalmines with seams worked from several horizons. The considerable capital outlay of driving horizons before production can begin is recouped by the advantage of having long straight level roadways of generous dimensions unaffected by the crushing effect of nearby extraction of the mineral.
23. What is the difference between engineering stress and true stress?
In biology, Stress is something that disrupts homeostasis of an organism. In engineering, Stress is an external force that pushes, pulls, twists, or otherwise puts force on something.
Engineering stress assumes that the area a force is acting upon remains constant, true stress takes into account the reduction in area caused by the force.
24. What is a kip?
1 kip = 1000 lbs
25. What are some structures that may be subjected to fatigue?
Bridges, hydraulic presses, burners trains
26. Will going from a 3-tap to 6-tap increase water pressure?
No, the pressure will be the same, you will get more volume only if your pumps can handle the GPM, to increase pressure you may need a booster pump or a single pump that is rated for your needs.
27. Why does the pressure increase under soil?
Soil pressure increases with depth due to the overburden or self-weight of the soil and due to loads imposed upon the soil.
For example, the pressure variation below the depth of soil is linear and the relation is given by pressure = unit wt * depth. As depth increases, there will be a linear increase in the soil pressure.
28. What is the distance between railway tracks?
4 feet, 8 1/2 inches
29. How high should the water tank be to provide a 60 PSI at base of this water tower?
138.60ft
2.31ft of water= 1 PSI
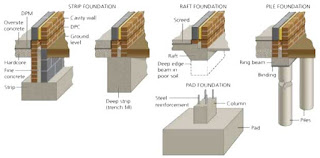
30. What are the reasons for geotechnical site investigations in Uganda?
To know the soil properties, in so doing be in position to determine whether the PArticular site is suitable for the purpose intended
To know the history of the site
To know what remedies need to be put in place before construction can start
Based on the soil properties, that can be determined on site and in the lab, design the appropriate foundation for the structure.
31. What do you mean by honeycomb in concrete?
Some people call it an air pocket in the concrete or a void.
32. What is the purpose of the gap in the road on this bridge?
Purpose of the gap in the road is to allow the road to exPAnd and contract with temperature changes without causing damage or deformation to the road.
33. What is the tensile strength of wood?
The tensile strength of a material is the value at which the material fails when subjected to a tensile force. (Tensile means a force pulling the wood fibers lengthwise, as opposed to a compressive force.) There are a lot of different types and load cases for wood, so there is not one answer to this question. For example,
wood used outside will fail at a lower load than wood inside. Wood is also anisotropic, i.e. it has different strength in different directions.
Example values of tensile strength vary anywhere from 175 pounds per square inch for Utility Grade pine to 1400 PSI for Dense Select Structural grade Douglas Fir. A
good reference for material strength data for most species and grades of commercially available wood can be found in the American Institute of Timber Construction handbook.
34. How many Lbs are there in a yard?
A pound (Lb) is a unit of measurement for weight while a yard is a unit of measurement for distance.
If you are referring to common measurements used on a construction site, a "yard" is a common abbreviation for a "cubic yard", which is a unit of measurement of volume. (A cubic yard equals 27 cubic feet.)
Since dirt weighs about 110 pounds per cubic feet, a cubic yard of dirt weighs about 2970 Lbs. Since concrete is heavier (150 PCF), a cubic yard of concrete weighs about 4050 Lbs.
35. What is a projection line?
Projection line is the way, in which the earth is shown on a flat piece of PAper.
36. What are moment of inertia and its importance in civil engineering?
The moment of inertia measures the opposition any kind of body will have against a certain momentum (along that same axis) trying to rotate that body.
37. What is the origin of name Railway Sleepers?
When sleepers were added below the railway, lines the trains ran more smoothly and people fell asleep on their journeys.
38. What is BMC stands for in BMC Software?
BMC Software founders Scott Boulett, John Moores, and Dan Cloer began a contract programming PArtnership that operated in and around Houston, Texas.
39. Does brick grows bigger every year.
Usually bricks do not grow, but since stuff gets all over, it looks like it grows.
40. How did street originate in the plumbing term street ell?
A "street ell" may have gotten its name because it describes a 90 fitting PArticularly useful in tight, street ditches. When installing water pipes under a street, or from a water service, again under the street, into a home or business, this street ell allows one to change pipe direction with one less fitting, and in less sPAce, than with a standard ell.
41. What is the absolute pressure scale?
Absolute pressure is calculated from a vacuum (0 PSI) and atmospheric pressure is14.7PSIa or 14.7 PSI above a vacuum 1PSI on a tire pressure gauge is called 1PSIg = 15.7PSIa 10PSIg=24.7PSIa 100PSIg=114.7PSIa etc.
42. What is the difference between QA and QC?
Many people and organizations are confused about the difference between quality assurance (QA), quality control (QC), and testing. They are closely related, but they are different concepts. Since all three are necessary to manage the risks of developing and maintaining software, it is important for software managers to understand the differences. They are defined below:
a) Quality Assurance: A set of activities designed to ensure that the development and/or maintenance process is adequate to ensure a system will meet its objectives.
b) Quality Control: A set of activities designed to evaluate a developed work product.
c) Testing is the process of executing a system with the intent of finding defects. (Note that the "process of executing a system" includes test planning prior to the execution of the test cases.)
43. How did the Romans get water up hills using aqua ducts?
Technically, the Romans were not able to get water to move uphill in a general sense. All aqueducts move water from an elevated source (spring-fed streams in the mountains) to end-users at a lower elevation. The water flows almost entirely downhill from the source to the end user. If the water needed to cross a valley, the Romans would build an arched structure with an elevated channel to cross the valley, but even this channel would have a vary slight downhill gradient that allowed water to flow towards the end user. If a large hill was in their way, the Romans would either divert the channel around the hill, dig a trench through the hill, or dig a tunnel through the hill, all while maintaining a fairly constant, slight downhill gradient towards the end user.
The only exception to the rule of a generally constant downhill slope to the water channel is that specific tunnel segments, the Romans could build the tunnel as an inverted siphon (mentioned above) to cross a depression or valley and raise the water level on the downhill side almost to the level of the uphill side. To do this requires a well-sealed tunnel strong enough to withstand the increased water pressure within the siphon. Note, however, that except for gaining a little bit of elevation if you slow down fast-moving water, you normally cannot get water to flow out of the outlet at a higher elevation than the inlet. So technically, even the Romans were not able to get water to flow "up a hill".
44. Will Water damage concrete?
As far as only concrete is concerned i.e. plain concrete, the effect of water seePAge is very little (depending upon the grade of concrete) whereas for RCC (reinforced cement concrete) water that seeps in corrodes the reinforcement and thus reduces the life of the structure. The defects that water seePAge induces in concrete are as follows:
a) induces capillary formation (due to the detiorating characteristics of water)
b) With this capillaries the concrete starts sPAlling out; i.e. the places where capillaries are formed, with even slight amount of stress that portion comes out and exposes the steel to the atmosphere
c) Concrete has a pH of about 12 -13. It also reduces the pH of the concrete when in salty water (or) when exposed to marshy areas.
d) Reduces the overall strength of concrete
e) Reduces durability
f) Reduces permeability to further water see Page
g) Results in ageing of structures
45. How do you determine Specific gravity of cement?
Cement is usually purchased as a powdery substance that is mixed with sand, aggregate, gravel, and water to form concrete. Since the cement itself is usually a powder, it is hard to measure a standard value for its specific gravity. In addition, since cement is usually not used by itself, knowing its specific gravity is not
Particularly useful.
A more useful question is "What is the typical density of concrete?" A rule of thumb answer is that normal cured concrete has a density of about 150 pounds per cubic foot. This includes the weight of the cement, sand, aggregate, and that PArt of the water that chemically binds with the cement to form the concrete. Since water weighs about 62.4 pounds per cubic feet, concrete is about 2.4 times as heavy. Thus, the specific gravity of concrete is about 2.4. If you took cement and mixed it with water, you would eventually have a hard lump of useless cement and it would also have a specific gravity of between 2 and 2.4.
46. What is the meaning of a blue land surveyors flag?
If the flag was placed by Utility personnel responding to a "One-call" locate request, the blue flag indicates a buried water line. You see these marked when a contractor calls the "Call before you dig number" a couple of days prior to excavating. This is required by law in each state to reduce the likelihood of damaging
underground utilities when excavating.
The standard color code used by almost all utility comPAnies for PAinting & flags is:
White - "Here is the area I plan on excavating!"
Blue - water line
Red -electricity
Yellow -natural gas
Green -sewer
Orange -telephone and/or fiber optic line
If the blue flagging was a fuzzy blue marker nailed to the top of a wood surveyor's stake, then it probably serves to indicate the top of the grade at which the engineer wants the earthmoving equipment to place fill dirt. These are called "blue-top" stakes.
47. What are advancements in civil engineering?
Unlike other fields of engineering, the major advancement of the filed has been in the early years of the century before the last century where the use of concrete technology is advanced. The use of cement as a construction material is since the turn of the last century, improvement in the field increase by the use of steel
elements in the construction of buildings and bridges of various types. With the help of two, it was possible to do multistory buildings in the world. Machineries were created to speed up the construction structures. The last century has also seen the advent of sophisticated design to withstand the effect of earthquake that was not possible before. With the use of computers, development of model and analysis of structures under the effect of loads was made possible. Before just two decades, it used to take months and months to design high-rise building and big bridges. Now it is a matter of hours.
48. Why is the statue of liberty made of copper?
Copper is a very durable material when exposed to weather and is soft enough that it can be easily molded to curved shapes such as those in the Statue of Liberty. It is also traditionally used in buildings for complex roofs, so there would have been trades people available trained to use it.
Other metals that can be molded are lead but it does not have the attractive verdigris color, and gold much is more expensive
49. Are cruise ships built for the transatlantic run?
The Queen Mary 2 was built for transatlantic crossings, but much smaller ships can make the crossing easily. In 1995, I crossed the Atlantic from New York to the Azores on the Royal Princess (which was not the same ship as the current Royal Princess), which was about one-fourth the size of the QM2. Just about any seaworthy Passenger ship can navigate the Atlantic safely, if not comfortably.
50. What is diversion tunnel in a dam?
When a dam is to be built, a diversion tunnel is usually bored through solid rock next to the dam site to byPAss the dam construction site. The dam is built while the river flows through the diversion tunnel.
51. What distance in meters on the ground is the equivalent of one second of arc in longitude or latitude?
One minute of arc as measured at the centre of the Earth covers one nautical mile on the surface of the Earth at mean sea level. One nautical mile is 6080 feet or 1853.2 meters. Therefore one second of arc would be 6080 / 60 = 101.3 feet or 30.886 meters.
Lines of latitude are at regular intervals PArallel to the equator. The relationship between degrees of latitude and the distance sPAnned on the earths surface remains constant. Therefore at all latitudes 1 minute of latitude sPAns 1 nautical mile on the earths surface.
Lines of longitude converge at the poles. Therefore, the relationship between degrees of longitude and the distance sPAnned on the earth�s surface is reduced as the poles are approached.
At the equator, the distance sPAnned by 1 minute of longitude would be 1 nautical mile. At the poles, it would be zero. To calculate the actual distance on the surface of the earth between two points of known latitude and longitude requires knowledge of spherical trigonometry to calculate the great circle distance between the two points.
The distances quoted are for the surface of the earth at mean sea level. Distances will be increased above sea level and reduced below it.
52. How do you maintain water pressure?
If you have water pressure and wish to maintain it, do not cause flow in the line, which will reduce pressure due to friction. To keep pressure up, reduce friction by increasing the line size or eliminating some other restriction.
53. What are some facts about concrete?
Actually, drying is not directly linked to hardness in concrete. After concrete is poured, putting it in a wet environment by spraying it constantly with water will hasten its hardening and its curing. After concrete cures, it is hard.
54. Who designed the city of Washington DC?
Pierre L'enfant
55. Where is the worlds longest elevator and how long is it?
Gold mines in South Africa go a few kilometers below the surface. The deepest mine now is the Mponeng Mine in the Orange Free State. The depth of the mine is well over 3000m from the surface and is getting deeper. The lift itself descends 3037m to a point 1200m below sea level. It takes 4 minutes.
56. How many kilo-Newtons equals 1000 kilogram?
When the 1000 kg are at rest, on Earth with gravitational acceleration 9.81 m/s2, 1000 kg equal 9.81 kN.
57. What does civil engineering mean?
They do many interesting things. Their job has to do a lot with design and construction. They can tell you what works and what will not for all sorts of situations.
There is a lot of mathematics involved along with many other disciplines. They have to have a good solid understanding of how the environment works and how nature interacts with man made. They are probably best known for designing bridges, interstates, skyscrapers, canals, and so forth.
58. How long does it take concrete to harden?
It takes 28 days to cure.
59. What is the biggest dam in America?
The Grand Coulee Dam - Grand Coulee, Washington
a) Length 5,223 ft
b) Height 550 ft
60. How does siphoning work?
Pretty good if the outside hose is a lot lower than the inside hose. The siphon works by a hose stuck in a fluid container higher than the receiving container. Suction is shortly placed on the lower side of the hose until the fluid is flowing down the down line. Gravity will cause a continued flow.
61. Why was the Empire State Building made of steel?
Strength--Steel is very strong
Flexibility--Ability to flex in the wind
Cost--Inexpensive and fast to build; prefab construction
Concrete, a possible alternative, has less compressive strength than steel. The bottom support structure of the empire state building would consist of a large percentage of solid concrete simply to support the weight of the building.
62. What is the quantity of cement in Mix M20 concrete?
For nominal Mix Cement consumption for M25 will be 570 kg per cum. and for Design Mix it can be optimized to 510 kg per cum.
63. What is unit weight of normal concrete?
145 PCF
64. What is the difference between shear and tensile strength?
Tensile Strength for a Bolt is determined by applying a Force along it long axis. Shear Strength for a Bolt is determined by applying a Force across its diameter, as it would be loaded in a lug joint.
65. How many Pyramid in Egypt?
About 80
66. Would you cause a 55-gallon drum of water to weigh more by climbing in?
A person will sink in water if he is not holding enough air in his lungs to keep him floating. Therefore, the person weighs more than the amount of water that he will displace.
67. Who built the sears tower?
While he did not build the structure (he died in l959), there is some evidence the idea was suggested under a different name (Illinois Building) by Frank Lloyd Wright, one of the few true skyscrapers in which he had a role. The original design for the Illinois Building would have topped off at 5,280 Feet! The Swears tower is a quarter of this at most, but there are similarities.
68. At what point does a circle start losing area when being flattened?
The area ratio decreases slowly at first then more rapidly.
The area of an ellipse is A=pi x a X b, a and b are the 1/2 major and 1/2 minor axis. If a = r = b the area is A=pi X r2, which is a circle. Not hard to graph this but you will have to write the area of the ellipse in terms of the circumference.
69. How do you compute volume of airflow?
Orifice meter is used for measuring flow rate air.
70. What is made from large rocks, which protects the base of cliffs?
Stacks
71. Why are the bolts that hold steel rails together in oval holes?
It has to do with the design of the bolts. The reason that head of the bolt is oval. The head of a bolt fit flush into the bar and set in opposing sets is so that a piece of dragging equipment will not shear off all the bolts in a joint but rather the just the nuts one side. As a result, if the hole were not oval on one side there
would be no way to tighten or loose the bolts in a joint.
72. What are the materials used in building a gravity dam?
There are many gravity dams constructed of comPActed earth. High dams are generally concrete. All dams require a spillway to be safe. The spillway must be armored.
73. How many feet are in 4 square yards?
There are 9 square feet in a square yard therefore there are 36 square feet in 4 square yards.
74. What black man invented the clothes dryer?
George T. Sampson
75. What is the average density of soil?
For purposes of civil engineering, an average soil will have a density of about 100 to 110 pounds per cubic foot. (This can vary a little depending upon how well compacted the soil is.)
76. What glue is least sticky?
Elmers glue is least sticky.
77. What are the strongest shapes in building?
The pillars
78. Which architectural movement is also known as Jazz Moderna?
Art nouveau
79. What is the withdrawal force of steel nails?
In engineering, the code-allowable withdrawal force is zero, because the wood expands and contracts over time and the nail pullout force can reduce to zero.
80. What is the strongest bridge for a school contest?
If you are making a spaghetti bridge, bunch it all together in a triangular prism or a big brick and just fill the gaps with Paste.
81. What is the formula for figuring out how many gallons of water are in a pipe by the foot?
0.61 * d2, where d is the diameter of the pipe in inches.
82. What is the tensile strength of marble?
Tensile Strength, Ultimate 7.00 - 20.0 MPA 1020 - 2900 PSI
this is the strength in a pure tension test. For bending use:
Modulus of Rupture 0.00410 - 0.0276 GPA 0.595 - 4.00 ksi
83. Did any of the Egyptian pyramids ever fall down?
Yes, many did. The great pyramid and others that have survived did so for a reason. Their shapes made them sturdier over time and were not the first design. Many steppe pyramids were built but were too steep and as the corners eroded, the whole pyramid fell under its own weight. They were built too steep and did not have the base structure as seen in the great pyramid.
84. Can a wave happen in the middle of the ocean like in the movie Poseidon 2006?
Yes. Rogue waves have been known to capsize ships.
85. What materials were used to build the Golden Gate Bridge?
Its materials were steel and concrete.
86. What is the density of most of construction materials?
If it floats it is less dense than water, 62.4 lbs/cubic ft. Wood is about 40 lbs/ cu.ft.--it floats. Concrete is 150 lbs. / cu.ft. -- It does not float.
87. How and where are aqueducts built?
Aqueducts are built in areas where you have a bunch of motivated end users (like a town or group of farmers) at a low elevation in need of a more reliable source of water located somewhere fairly nearby at a higher elevation. The aqueduct builders construct a series of canals, elevated channels, and tunnels as required to get the water from the source to the end users. Some good examples:
a) Roman engineers built aqueducts throughout Italy and France from mountain water sources to serve city dwellers
b) Water-needy Southern California cities and farms are served by an aqueduct that brings them water from sources in Northern California
c) New York City is supplied by an aqueduct and tunnel system from sources upstate.
d) Inca farmers in coastal valleys built irrigation aqueducts from sources higher up in the Rockies
e) Native American cultures in Phoenix area built irrigation canal systems that diverted water from sources at higher elevations to irrigate their crops.
88. What does civil status mean?
Civil means like, when you do not get on with someone, but only talk when you have to. Alternatively, when you do talk you do not argue. Alternatively, if you are with someone who is of your both friends and family, you do not ruin it for them.
89. What are the advantages and disadvantages of lead products in construction?
Disadvantages: -Lead is very toxic; its use can result in pollution of the ground and more importantly of water supplies. This leads to the contamination of drinking water and can cause hazards to human health as well as disrupting entire ecosystems.
Advantages: Because of its toxicity, lead is being bought less and less around the world, which of course results in the lowering of its cost. In addition, lead melts at a relatively low temperature, making it great for solder. However, recently the Chinese have show an interest in buying mass quantities to manufacture batteries made from a base of lead so the price of this metal may soon rise.
90. How do you measure water flowing through 300 mm diameter pipes?
Same as in inches 3.14159265 and PSI have to be known.
Explain the various stages of the project planning process in construction.
First stage could be Briefing and Inception.
91. How do you convert wind speed into force?
Thermometer
92. What is kn measurement?
kn (both letters lowercase) is knots, which is a speed nautical miles per hour.
93. What are the advantages of building a dam on the river Nile?
It is the same as building a dam on any river. Dams are built to control flooding downstream during the wet season, generate power year round, and provide irrigation in the dry season.
94. How much does the leaning tower of Pisa lean?
About 14 feet
95. What is the best type of wood glue?
Noob
96. What are the uses of Groynes?
They prevent, or slow down erosion, and stop long shore drift. This, however, can have bad knock-on effects somewhere near.
97. What are the functions of a column in a building?
A column is used to support the weight of the roof and/or the upper floors. Now days, many columns are used for decorative purposes. A column along with load bearing beams can support a lot of weight.
98. What is an ice dam sock?
If you have never used a ice dam melting sock on your roof before, you will find that they provide an inexpensive method for removing roof ice dams and improving your home's heating efficiency. Roof ice dams are an annoying source of roof damage, leaks, and heat loss in the winter. The main causes are drip melt from improperly capped warm air vent pipes and poor roof insulation. Laying a ice melt sock onto the roof so it crosses the ice dam and overhangs the gutter, will melt through the snow and ice and create a channel for water to flow down into the gutters or off the roof. If done properly those ice sickles that form as the snow melts from the edges of the gutters will never appear, they too are a cause of much damage and are dangerous to life and limb.
99. What Tor stands for in Tor steel?
The owners last name
100. When was the first motorway built in England?
The first motorway opened in Britain was the M6 (M=Motorway). It was known as the Preston ByPAss. It was opened in 1958.
When it was planned, the Preston ByPAss was seen as the first piece of a large network. It was deemed a success and led to the construction of a second motorway, the M1, opened in 1959.